Security serves as a crucial aspect of any business environment. Protecting sensitive data, ensuring network integrity, and defending against cyber threats are essential tasks. Organizations must implement strong security principles to safeguard their systems and information effectively.
This article explores basic security concepts, highlights their applications, and shares practical insights. Understanding these principles is vital for organizations aiming to enhance their security measures. By prioritizing security, businesses can build trust and resilience within their systems.
Understanding the Key Security Principles
At the heart of any security system is a strong security architecture. This foundation is built upon key principles such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. These three pillars form the basic security concepts that all organizations, regardless of size, need to understand.
- Confidentiality: Ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to those who are authorized users.
- Integrity: Maintaining the accuracy and trustworthiness of data over its lifecycle.
- Availability: Ensuring that information and resources are available when needed by the right people.
These principles are crucial for implementing security systems that align with industry standards and fulfil regulatory obligations.
Types of Cyber Attacks
Cyber threats come in various forms, often categorized into two major types: active attacks and passive attacks. Understanding these is critical for threat modelling and designing effective defences.
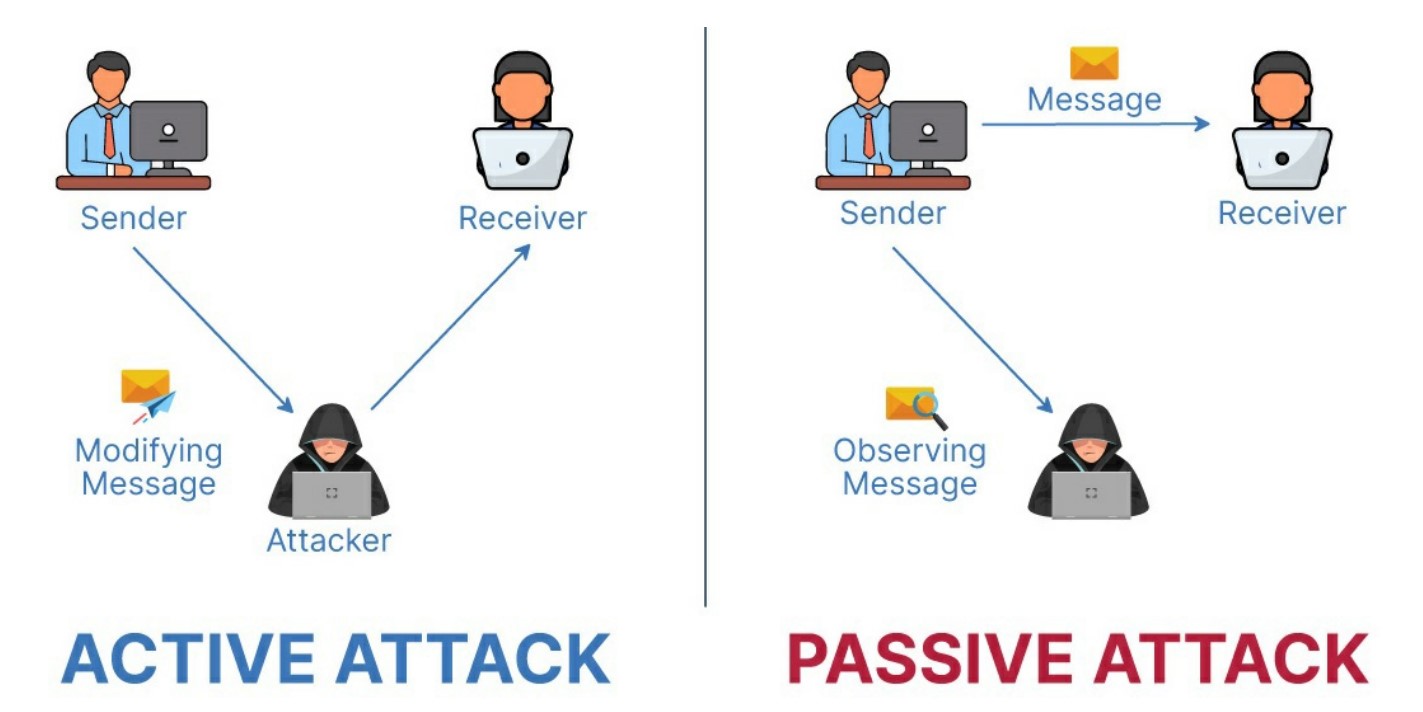
-
Passive Attacks
In passive attacks, the attacker eavesdrops on network communications without altering them. These attacks are usually stealthy and hard to detect. They exploit systems vulnerable to unauthorized monitoring, leading to information breaches.
-
Active Attacks
In contrast, active attacks involve direct interference with system resources, where an attacker may attempt to alter, delete, or even damage the data. Examples include denial-of-service attacks, which overload a system’s resources, making them unavailable to users.
Both attack types exploit security vulnerabilities in a system, and protecting against them requires implementing strong security measures and a strong security architecture.
Role of Access Control in Security
One of the most effective ways to mitigate cyber threats is through robust access control policies. Access control determines who can access what within a system. By employing role-based access control (RBAC) or even newer models like the typed access matrix model, organizations can tightly manage and monitor user access.
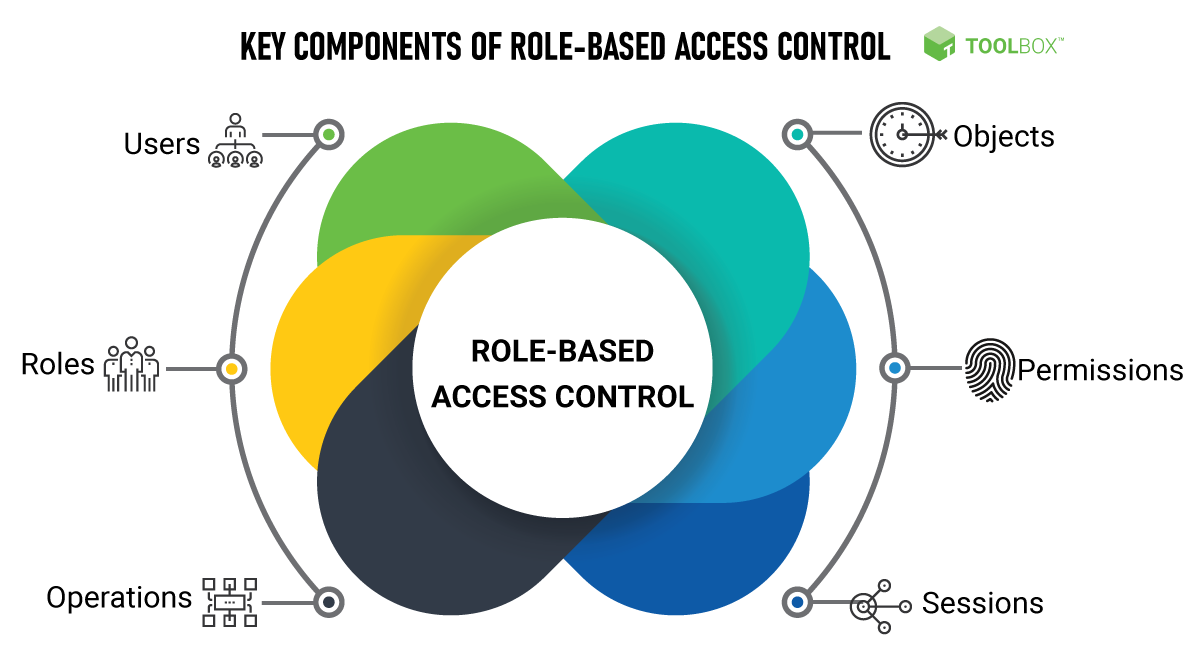
Implementing Access Control Systems
- Access permissions: Ensuring that only secure users with appropriate access rights can retrieve or modify sensitive data.
- Access behaviour: Monitoring and managing how authorized users interact with sensitive systems, reducing the risk of data breaches.
Access management is vital for securing user accounts, mobile devices, and even network devices. Regular audits and updates to access permissions categories help ensure that employees have the correct permissions without unnecessary access, mitigating potential insider threats.
Encryption
Encryption plays a central role in modern security by protecting data from unauthorized access, both during transmission and when stored. Two fundamental encryption techniques are used to secure data:
- Symmetric Encryption: This method uses a single key for both encryption and decryption. It’s efficient for encrypting large amounts of data quickly.
- Asymmetric Encryption: This method uses a pair of public and private keys. While more secure than symmetric encryption, it is also computationally heavier.
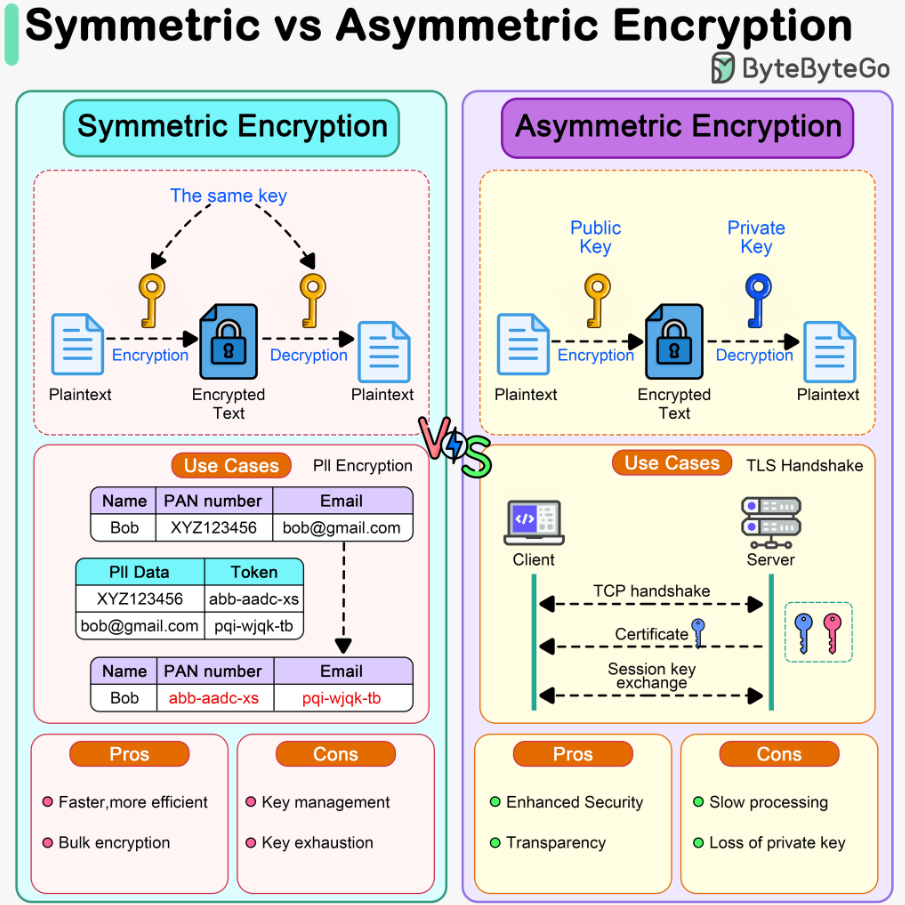
Encryption ensures that data remains secure, even if a malicious party gains access to it. Implementing strong encryption methods such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is an industry best practice.
Furthermore, the use of digital certificates and authority-signed certificates ensures that websites and systems are authenticated by trusted entities. Companies like DotsDen rely on these certificates for secure server authentication and mutual authentication between users and systems.
Endpoint Security and Securing Network Systems
As businesses increasingly rely on internet-based services, securing individual endpoint security measures becomes critical. These measures include securing workstations, servers, and mobile devices connected to the network.
Types of Attacks Targeting Endpoints
- Malware attacks: These involve the installation of malicious programs, like viruses or ransomware, on an endpoint.
- Persistent Threats: These are prolonged and sustained attacks that slowly infiltrate an entire network.
Implementing robust endpoint security measures, such as firewalls, anti-virus software, and intrusion detection systems, significantly reduces the risks of these attacks.
The Importance of Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Passwords alone are no longer enough to protect user accounts. Weak or compromised passwords are one of the biggest security threats. Two-factor authentication (2FA) provides an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through a second method, such as a phone number or email, in addition to their login credentials.
By combining 2FA with encryption and other security controls, businesses can ensure more comprehensive protection for their systems and data.
Common Types of Cybersecurity Threats
In the cybersecurity field, organizations face a wide range of common types of threats. These include:
- Phishing: Attackers attempt to trick individuals into providing sensitive information, usually via email attachments disguised as legitimate.
- Social Engineering: Manipulating people into performing actions or divulging confidential information.
- Malware: Malicious software designed to harm or exploit systems.
Addressing these types of attacks requires effective information security practices, such as continuous training for staff, secure storage devices, and the use of security protocols.
Building a Security Culture
Creating a culture of security within an organization involves more than just implementing technology solutions. It requires educating employees and establishing security practices across all levels.
Security Practices for Organizations
- Security Training: Regular cybersecurity training helps employees understand the types of network security measures in place and how to follow them.
- Disaster Recovery Plans: Developing a comprehensive disaster recovery strategy to protect against natural disasters and system failures.
- Strong Password Policies: Enforcing the use of strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
- Malware Protection: Installing anti-malware software and keeping it up to date to defend against malicious code and other threats.
By prioritizing these security concepts, businesses can reduce the likelihood of breaches and ensure they are well-prepared to face potential threats.
Final Thoughts
Security is a multifaceted challenge, but by focusing on the fundamental principles of cybersecurity, organizations can significantly improve their defences. From implementing encryption techniques to reinforcing access control policies, maintaining strong security systems is vital for protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with protection regulations.
For businesses aiming to enhance their security posture, services from DotsDen provide tailored support in areas like network security, encryption, and access control, helping organizations secure their data and systems with industry standards in mind. By applying the concepts discussed in this article, you can safeguard your business from a wide range of cybersecurity challenges.

